Why Sodium-Ion Batteries Are Terrible For Solar Storage
These days just about any battery storage solution connected to PV solar or similar uses LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries. The reason for this is obvious: they got a very practical charge and discharge curve that chargers and inverters love, along with a great round trip efficiency. Meanwhile some are claiming that sodium-ion (Na+) batteries would be even better, but this is not borne out by the evidence, with [Will Prowse] testing and tearing down an Na+ battery to prove the point.
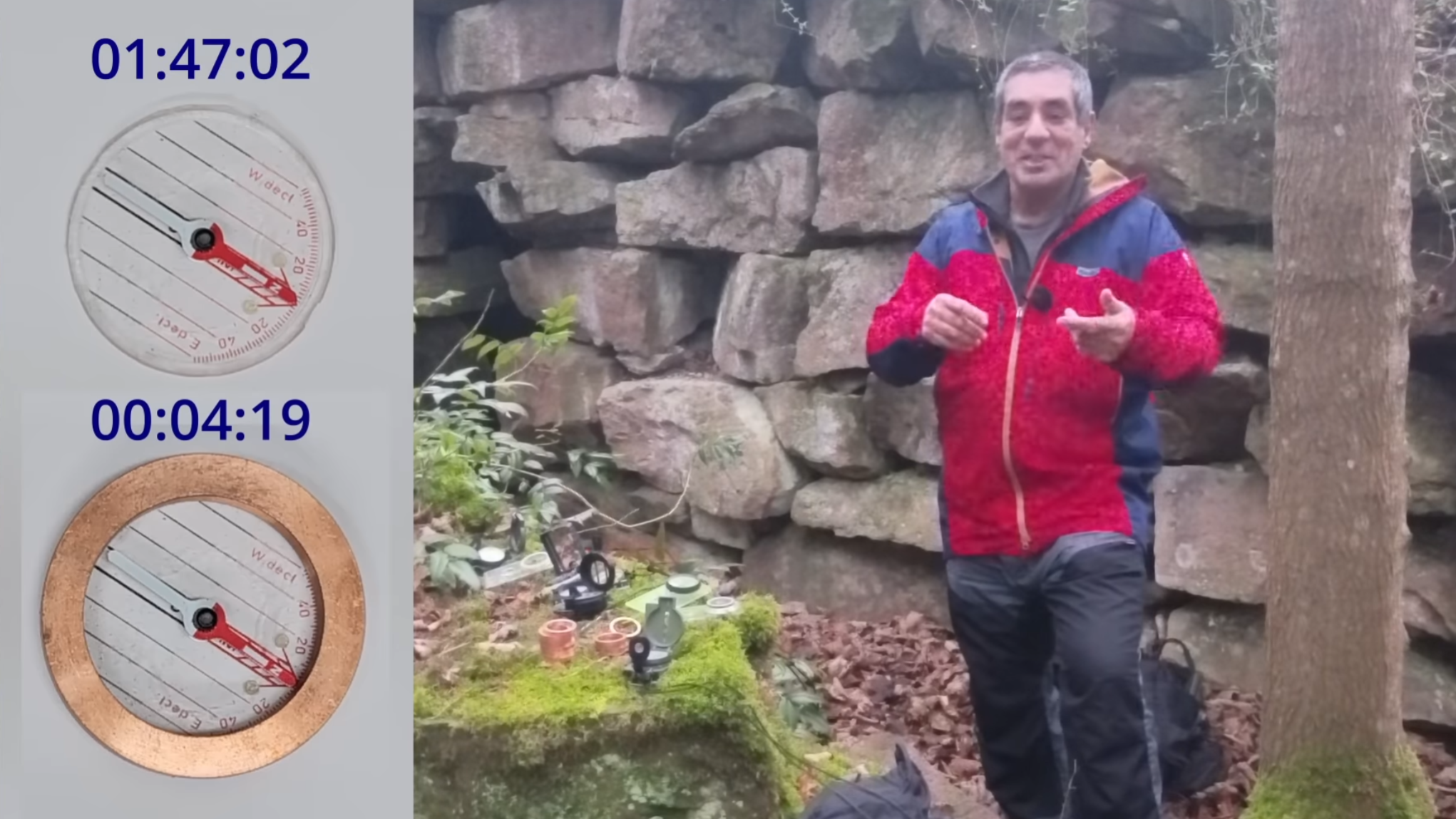
The Hysincere brand battery that [Will] has on the test bench claims a nominal voltage of 12 V and a 100 Ah capacity, which all appears to be in place based on the cells found inside. The lower nominal voltage compared to LFP’s 12.8 V is only part of the picture, as can be seen in the OCV curve. Virtually all of LFP’s useful capacity is found in a very narrow voltage band, with only significant excursions when reaching around >98% or <10% of state of charge.
What this means is that with existing chargers and inverters, there is a whole chunk of the Na+ discharge curve that’s impossible to use, and chargers will refuse to charge Na+ batteries that are technically still healthy due to the low cell voltage. In numbers, this means that [Will] got a capacity of 82 Ah out of this particular 100 Ah battery, despite the battery costing twice that of a comparable LFP one.
Yet even after correcting for that, the internal resistance of these Na+ batteries appears to be significantly higher, giving a round trip efficiency of 60 – 92%, which is a far cry from the 95% to 99% of LFP. Until things change here, [Will] doesn’t see much of a future for Na+ beyond perhaps grid-level storage and as a starter battery for very cold climates.



Post Comment